ARCIMBOLDO_BORGES tutorial
Aims of the tutorial
In this tutorial, we will show how to launch ARCIMBOLDO_BORGES in order to
1. Create a library
2. Use that library against experimental diffraction data to solve a structure and to analyze the resulting output
This example uses the latest ARCIMBOLDO_BORGES released on November 2016.
Data tutorial
Experimental details

Bioinformatics predictions
Secondary structure prediction analysis is useful to define an initial hypothesis as to local folds present in our structure. For example, the secondary structure prediction may suggest the presence of beta sheets with at least three strands, even if we do not know if they will be parallel, antiparallel, or mixed parallel-antiparallel. In that case, BORGES offers the possibility of automatically performing initial assessment with subsets of libraries to prioritize starting hypotheses according to MR FOMs or follow the order of the most frequent folds.
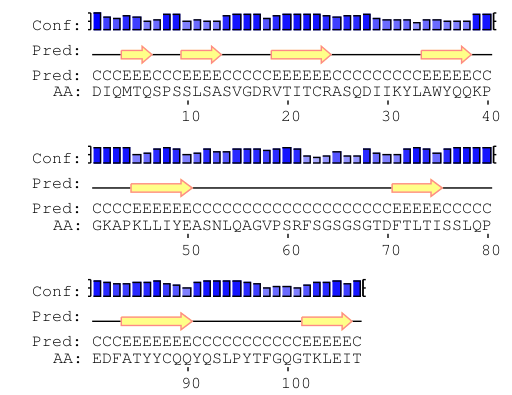
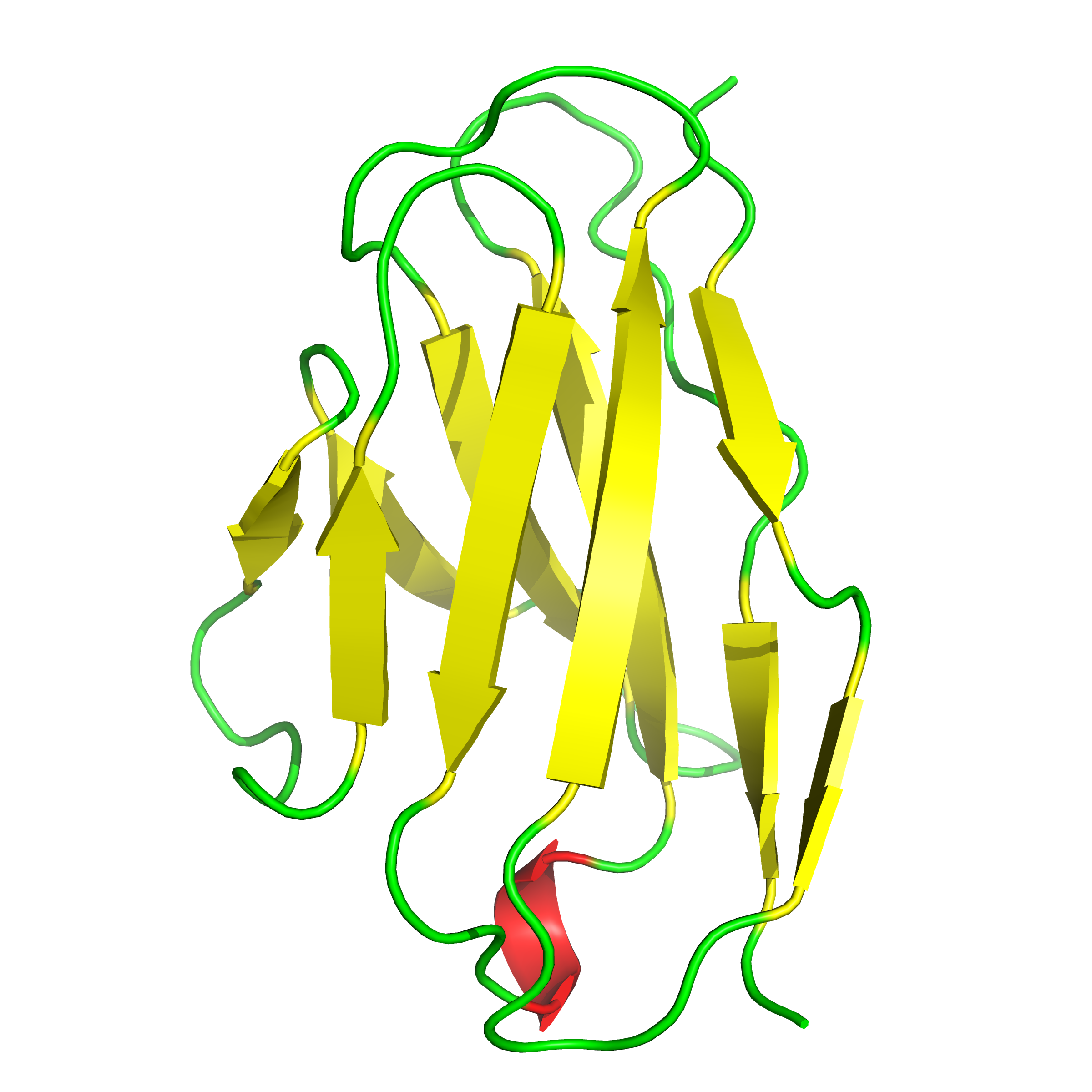
In our case, as the protein is an immunoglobulin kappa-light chain domain, it must contain antiparallel β-sheets, and secondary structure prediction done with PSIPRED and shown in the figure agrees, so we will be creating and using an antiparallel beta-sheet library.
Step by Step tutorial
1. Creation of a BORGES library
In order to solve a structure using ARCIMBOLDO_BORGES we need at least one library. This library will contain all superimposed models retrieved from the database that fulfill geometrical conditions defined by the user (i.e. 2 contiguous parallel alpha helices of 16aa or three antiparallel beta strands within set thresholds). The library is created with a novel algorithm in ARCIMBOLDO_BORGES that allows to extract not only alpha helices and beta strands, but also coils and loops. This new algorithm is still under development and will be described soon.
2. Usage of the library against experimental data to solve the structure
Data preparation and data conversion
For this tutorial we will need only the reflection file in two formats (.mtz and .hkl). All required files, including the library, can be downloaded here. If you have an hkl file you can use the programs F2MTZ and TRUNCATE or generate a .sca file and use SCALEPACK2MTZ. On the contrary, if you have an mtz file you can use MTZ2HKL to get your hkl file. For runs of ARCIMBOLDO_BORGES on helical fragments you will need to provide the mtz file in P1 space group in order to be use Paterson Correlation Refinement of rotations.
Input
- An mtz file containing the reflection data
- A SHELX reflection file hkl containing the reflection data
- The configuration .bor file
[CONNECTION]: distribute_computing: local_grid setup_bor_path: /path/to/setup.bor [GENERAL]: working_directory: /path/to/working_directory mtz_path: %(working_directory)s/4l1h.mtz hkl_path: %(working_directory)s/4l1h.hkl [ARCIMBOLDO-BORGES] name_job: 4l1h molecular_weight: 13000 number_of_component: 1 rmsd: 0.2 i_label: IOBS sigi_label: SIGIOBS shelxe_line: -m30 -s0.6 -v0 -a6 -t10 -o library_path: /absolute/path/to/the/library/ prioritize_phasers: True
The [CONNECTION] section contains the information about the type of run and about the general configuration instructions. In this case, we are going to use the local grid defined in the configuration file setup.bor.
The molecular weight, number of component and percentage of identity should be defined for PHASER to perform our search.
As clusters in the library will be further grouped after the results of an initial fast rotation function (FRF), we can choose if we want to try all or select a subset (defined by a list of numbers separated by commas).
Arguments for the SHELXE command line must be given.
On the library path you have to put the absolute path to where the library of beta sheets is located.
Execution
To launch ARCIMBOLDO_BORGES you can again choose between:
1. Interactively:
ARCIMBOLDO_BORGES conf_file.bor
2. In background:
nohup ARCIMBOLDO_BORGES conf_file.bor >& logfile.log&
Output: Did it work? What may I change?
On the working directory, an html file called as the job. It is written while the program is running and updated as results are obtained. You may use this information for manual intervention (stopping the run, reparameterizing). If left to run, ARCIMBOLDO_BORGES will sequentially try the best clusters (green ones in the html, based on number of models and figures of merit). Once a solution is found (SHELXE traced mainchain CC > 30%), it stops after some recycling steps to improve it.
What we have in our
4l1h Output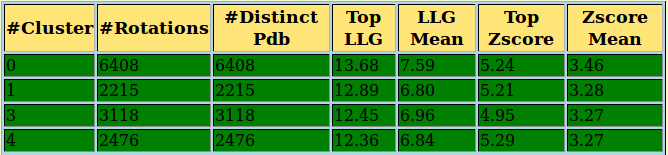
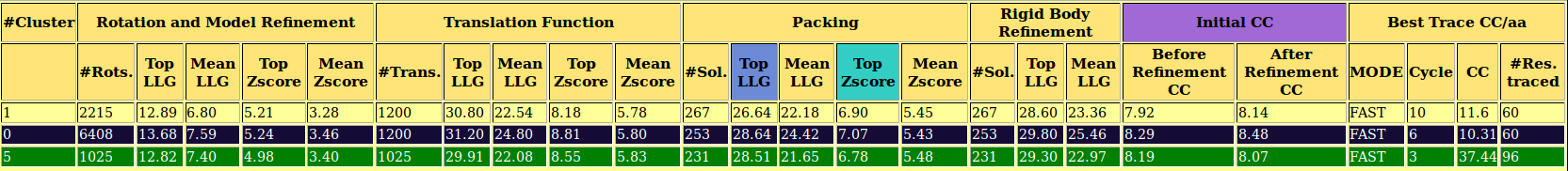
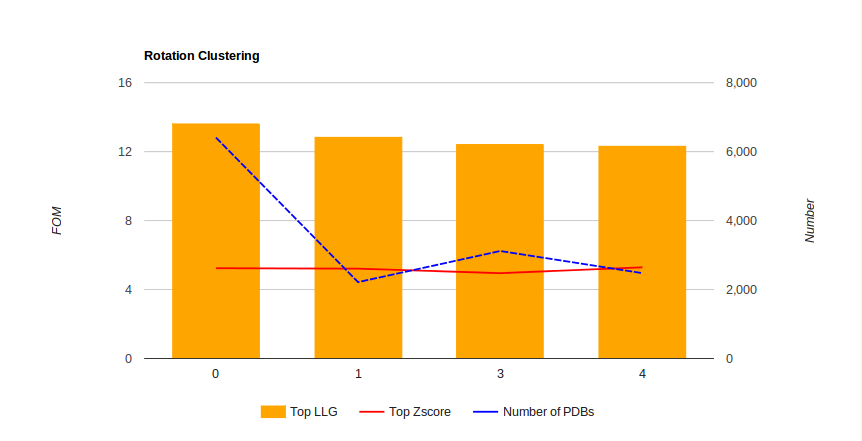
- An interactive table where we can see the total number of rotation clusters and its FOMs by clicking on Show All. Otherwise, only the ones coloured in green, and that correspond to the most populated ones and with best FOMs, will be shown.
- An interactive graph showing the information on the previous table and again with the possibility of just showing the clusters that will be tried automatically.
- A large table with the characteristics and FOMs for each step and cluster, that is updated each time new results are obtained.
- The backtracing for the current best solution
- The links to the pdb of the best solution and its map